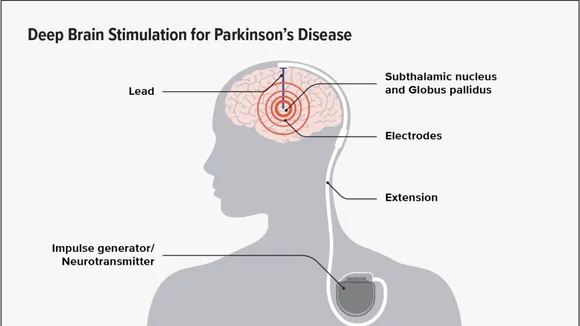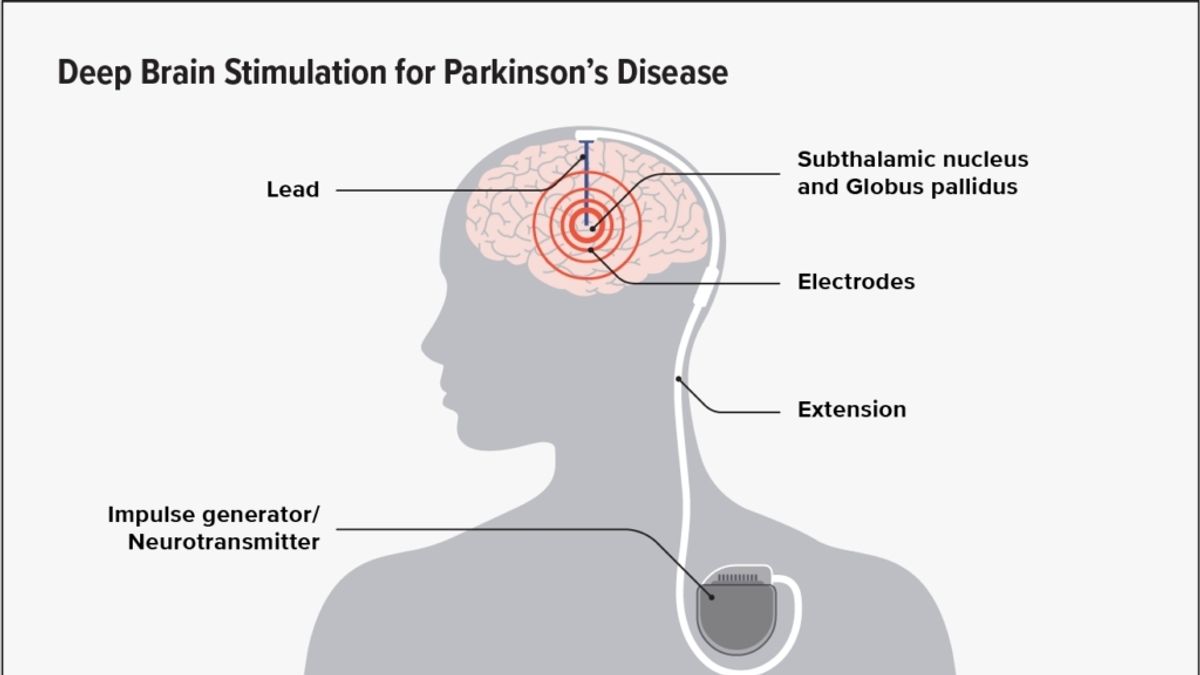
Recent advancements in the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease (PD) have uncovered the significant role of Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation (STN DBS) in promoting mitophagy and enhancing neuroprotection. This novel approach offers hope for mitigating the debilitating effects of PD by addressing mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, key contributors to the disease’s progression. The study’s findings, emphasizing the importance of timing, methodology, and the potential for long-term benefits, mark a pivotal shift towards more effective PD management strategies.
Understanding STN DBS: A Glimpse into Mechanisms
The study meticulously analyzed the impact of STN DBS on mitochondrial volume, numbers, and the preservation of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) of PD brains. Utilizing both rodent models and non-human primates, the research demonstrated that STN DBS enhances mitophagy through an mTOR-dependent pathway, subsequently reducing oxidative stress and apoptogenic factors. This intricate process underlies the dopaminergic neuroprotection attributed to STN DBS, offering insights into its therapeutic potential.
Methodological Precision: From Mice to Monkeys
The research methodology spanned from selecting optimal time points for lead implantation in mice models, based on dopaminergic neuron loss and motor impairment, to evaluating the therapeutic efficacy of STN DBS in non-human primates. The inclusion of NHPs, due to their closer similarity to humans, alongside rodents and human specimens, provided a comprehensive understanding of STN DBS’s effects across different species. The study’s rigorous approach, including assessments of motor performance, dopaminergic neuron preservation, and mitochondrial integrity, underscores the importance of precision in advancing PD treatment.
Implications and Future Directions
The findings of this study not only highlight the neuroprotective effects of STN DBS but also pave the way for further exploration into its long-term benefits and mechanism of action. The observed modulation of the mTOR pathway and its impact on mitochondrial dynamics suggest a promising avenue for therapeutic intervention in PD. As research continues to delve into the nuances of STN DBS, the potential for developing more effective, targeted treatments for PD becomes increasingly tangible, offering hope to those affected by this challenging neurological disorder.