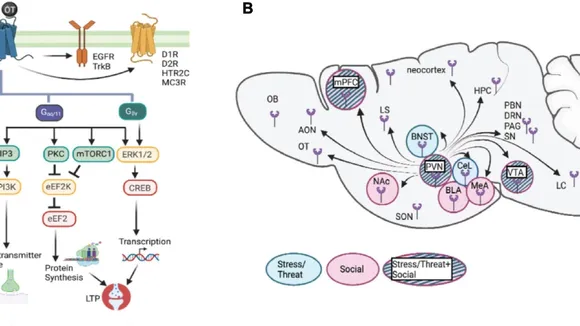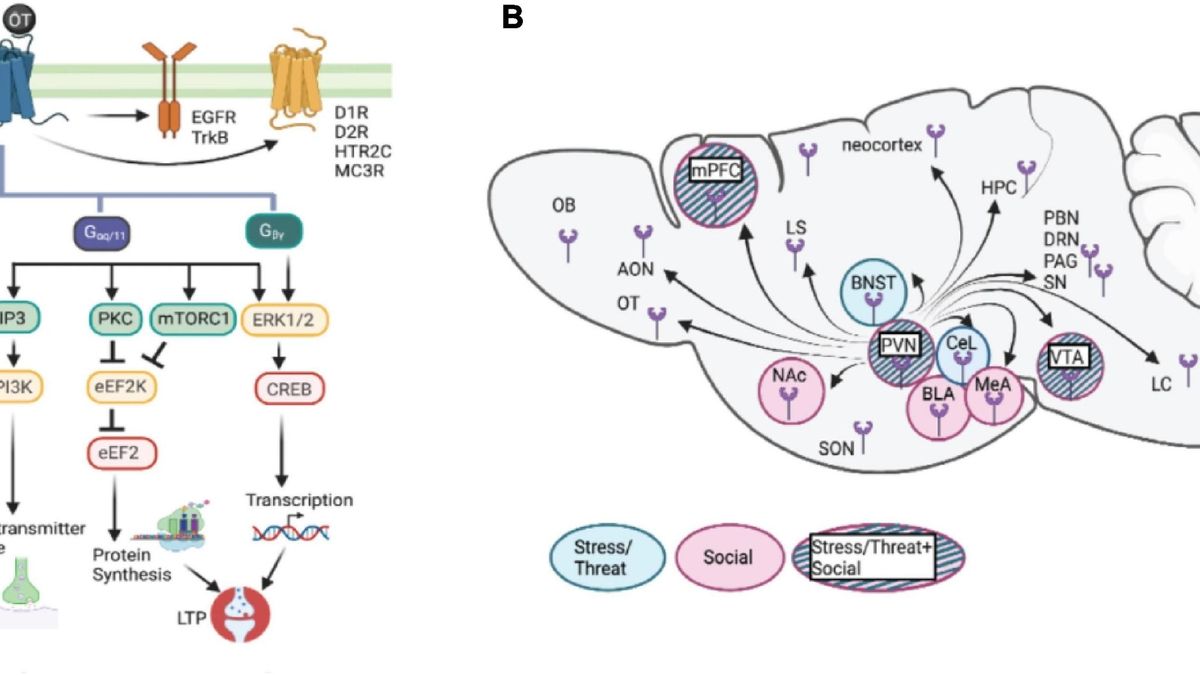
Recent research has shed new light on the role of two crucial neurotransmitters, dopamine and serotonin, in human social behavior. This pioneering study, conducted with Parkinson’s disease patients, has revealed a previously unknown neurochemical mechanism underlying human decision-making processes based on social context. Beyond expanding our understanding of human cognition and behavior, these findings have potential implications for understanding and addressing Parkinson’s disease pathology.
The Groundbreaking Study
The study involved four Parkinson’s disease patients who underwent a surgical procedure involving the bilateral implantation of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) electrodes in the subthalamic nucleus of each hemisphere. This unique patient group provided a rare opportunity to record and measure neurotransmitter fluctuations directly from the human brain.
Once implanted with the DBS electrodes, the participants engaged in the ‘ultimatum game,’ a two-person social experiment that probes norms of fairness. This ‘take-it-or-leave-it’ game allowed researchers to measure the impact of social context on neurotransmitter levels, specifically dopamine and serotonin. To accurately record these fluctuations, electrochemical recordings were made using a highly sensitive carbon-fibre electrode, providing direct evidence of fast changes in dopamine and serotonin reflecting context and value signals during social interaction.
A Novel Approach to Analyte Inference
Another innovative aspect of this study was the use of a statistical approach to analyte inference using an ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks. This cutting-edge method offers several advantages over traditional approaches in terms of accuracy, efficiency, and the ability to handle large and complex data sets. This detailed Fast-Scan Cyclic Voltammetry (FSCV) protocol and statistical modeling approach were outlined in the study, demonstrating the potential of such advanced analytical tools in future neurochemical research.
Implications for Understanding Social Behavior and Parkinson’s Disease
The research findings not only reveal a new neurochemical mechanism for human decision making based on social context but also offer fresh insights into the biological basis of human social behavior. By showing how dynamic interactions between dopamine and serotonin impact cognition and behavior, the study contributes to our understanding of the neurobiological underpinnings of social behavior.
Furthermore, as the study was conducted with Parkinson’s disease patients, these findings may also have significant implications for understanding and addressing the pathology of Parkinson’s disease. Dopamine, in particular, is known to play a crucial role in Parkinson’s disease, and this research could open up new avenues for treatment strategies.
Further Research on Dopamine and Behavioral Disorders
Interestingly, another recent study has explored the involvement of the prefrontal cortical dopaminergic system in the psychopathology of epilepsies and co-morbid conditions such as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). This research further supports the central role of dopamine in various neurological and behavioral disorders, reinforcing the necessity for continued research in this field.
In conclusion, this groundbreaking research has unveiled a new layer of complexity in our understanding of human social behavior and the role of key neurotransmitters. It is a significant step forward that has the potential to shape future research and treatment approaches in neurology and neuropsychiatry.
This was shown first on: https://medriva.com/health/the-role-of-dopamine-and-serotonin-in-human-social-behavior-insights-from-parkinsons-disease-patients